 FAQ
FAQ
38. Introduction to flame retardant standards
Flame retardant cable, as the name implies, means preventing the spread of flames. Flame retardant also has
corresponding standards to classify it.
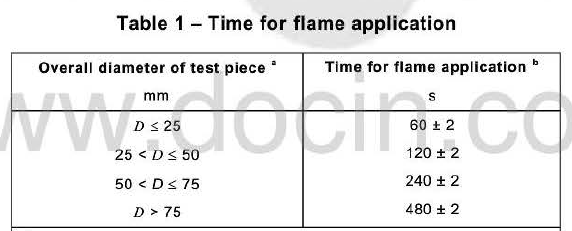
Flame retardant tests include single-cable burning test and bundled burning test. IEC 60332-1-2 is a vertical
burning test for a single cable. Take a 600mm cable sample, and the burning time is proportional to the outer
diameter of the cable
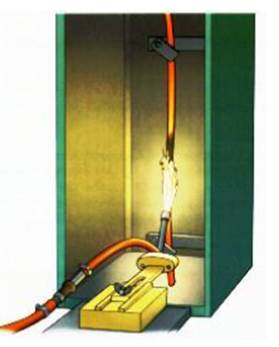
After the burning is over, if the distance between the lower edge of the upper fixture and the starting point of
the carbonized part is greater than 50mm, and the distance between the carbonized point where the burning
extends downward and the lower edge of the upper fixture is less than 540mm, the test is considered to have
passed.
IEC 60332-3 is a bundle burning test, and each sample line is at least 3.5m. As for how many lines there are in
this bundle, it needs to be calculated based on the non-metallic content of each meter of cable. IEC 60332-3-22,
which is what we usually call 3A, requires a non-metallic content of 7 liters per meter of sample and a burning
time of 40 minutes. IEC 60332-3-23, also known as 3B, requires a non-metallic content of 3.5 liters per meter of
sample and a burning time of 40 minutes. IEC 60332-3-24, which we call 3C, requires a non-metallic content of
1.5 liters per meter of sample and a burning time of 20 minutes. After the fire source is removed, if the
carbonization length is no more than 2.5 meters, it is considered to have passed the test. Therefore, 3A is more
difficult to pass the test than 3C because it contains more flammable non-metals and takes longer to supply fire.








