| Submarine Cables | |||
| Low Voltage Water Blocked Cables | Medium Voltage Submarine Cables | High Voltage Water Blocked Cables |
![]() Submarine Cables
Submarine Cables
XLPE Insulated DC High-Voltage Submarine Cable
Applications
These submarine cables are used for power transmission to offshore islands, oil platforms or to cross-rivers and
lakes. Cable design based on the mayor national or international standards e.g. VDE, IEC and ICEA or according
to customers design and standards.
Construction
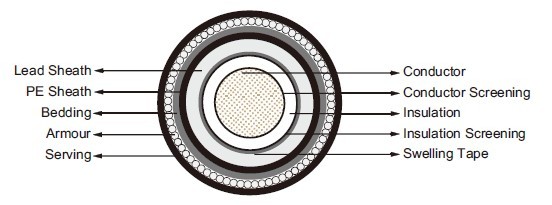
Conductor:Copper conductor, water blocked.
Conductor Screening: Extruded semi-conductive compound.
Insulation: XLPE.
Insulation Screening: Extruded semi-conductive compound.
Separator: Swelling tape.
Core Sheath1: Lead Sheath.
Core Sheath2: PE sheath.
Bedding: Bedding layer.
Armour: Galvanized steel wires filled with bitumen compound.
Serving: Polypropylene yarn.
Electrical Data:
127/220(245) kV
| Nominal Cross Section Area |
Capacitance | Inductance | Charging Current per phase @50Hz |
| mm² | μF/km | mH/km | A/km |
| 500 | 0.14 | 1.42 | 5.8 |
| 630 | 0.16 | 1.40 | 6.4 |
| 800 | 0.17 | 1.37 | 6.9 |
| 1000 | 0.19 | 1.35 | 7.4 |
| 1200 | 0.20 | 1.33 | 7.8 |
| 1400 | 0.21 | 1.32 | 8.2 |
| 1600 | 0.22 | 1.31 | 8.6 |
160/275(300) kV
| Nominal Cross Section Area |
Capacitance | Inductance | Charging Current per phase @50Hz |
| mm² | μF/km | mH/km | A/km |
| 500 | 0.14 | 1.42 | 6.8 |
| 630 | 0.16 | 1.40 | 7.7 |
| 800 | 0.17 | 1.37 | 8.3 |
| 1000 | 0.18 | 1.35 | 9.0 |
| 1200 | 0.19 | 1.33 | 9.5 |
| 1400 | 0.20 | 1.32 | 10.0 |
| 1600 | 0.21 | 1.31 | 10.4 |
200/345(362) kV
| Nominal Cross Section Area |
Capacitance | Inductance | Charging Current per phase @50Hz |
| mm² | μF/km | mH/km | A/km |
| 630 | 0.14 | 1.40 | 8.8 |
| 800 | 0.15 | 1.37 | 9.7 |
| 1000 | 0.17 | 1.35 | 10.7 |
| 1200 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 11.1 |
| 1400 | 0.19 | 1.32 | 11.6 |
| 1600 | 0.20 | 1.31 | 12.1 |
230/400(420) kV
| Nominal Cross Section Area |
Capacitance | Inductance | Charging Current per phase @50Hz |
| mm² | μF/km | mH/km | A/km |
| 630 | 0.13 | 1.40 | 9.6 |
| 800 | 0.15 | 1.37 | 10.7 |
| 1000 | 0.16 | 1.35 | 11.7 |
| 1200 | 0.18 | 1.33 | 12.9 |
| 1400 | 0.19 | 1.32 | 13.5 |
| 1600 | 0.19 | 1.31 | 14.1 |
Dimension and Weight:
127/220(245) kV
| Nominal Cross Section Area |
Nominal Conductor Diameter |
Nominal Insulation Thickness |
Nominal Diameter Over Insulation |
Nomanal Lead Sheath Thickness |
Nominal Overall Diameter |
Weight |
| mm² | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/m |
| 500 | 26.2 | 24.0 | 77.6 | 2.9 | 111.0 | 29.3 |
| 630 | 29.8 | 23.0 | 79.2 | 3.0 | 112.8 | 31.2 |
| 800 | 33.7 | 23.0 | 83.1 | 3.1 | 117.5 | 34.5 |
| 1000 | 37.9 | 23.0 | 87.3 | 3.1 | 121.9 | 37.7 |
| 1200 | 41.2 | 23.0 | 90.6 | 3.1 | 125.2 | 40.4 |
| 1400 | 44.4 | 23.0 | 93.8 | 3.1 | 128.6 | 43.2 |
| 1600 | 47.4 | 23.0 | 96.8 | 3.1 | 131.8 | 46.0 |
160/275(300) kV
| Nominal Cross Section Area |
Nominal Conductor Diameter |
Nominal Insulation Thickness |
Nominal Diameter Over Insulation |
Nomanal Lead Sheath Thickness |
Nominal Overall Diameter |
Weight |
| mm² | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/m |
| 500 | 26.2 | 26.0 | 81.6 | 3.0 | 115.2 | 31.1 |
| 630 | 29.8 | 24.0 | 81.2 | 3.0 | 114.8 | 31.8 |
| 800 | 33.7 | 24.0 | 85.1 | 3.1 | 119.5 | 35.2 |
| 1000 | 37.9 | 24.0 | 89.3 | 3.1 | 123.9 | 38.4 |
| 1200 | 41.2 | 24.0 | 92.6 | 3.1 | 127.4 | 41.6 |
| 1400 | 44.4 | 24.0 | 95.8 | 3.1 | 130.6 | 44.4 |
| 1600 | 47.4 | 24.0 | 98.8 | 3.1 | 133.8 | 47.2 |
200/345(362) kV
| Nominal Cross Section Area |
Nominal Conductor Diameter |
Nominal Insulation Thickness |
Nominal Diameter Over Insulation |
Nomanal Lead Sheath Thickness |
Nominal Overall Diameter |
Weight |
| mm² | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/m |
| 630 | 29.8 | 28.0 | 89.2 | 3.1 | 123.4 | 35.2 |
| 800 | 33.7 | 27.0 | 91.1 | 3.1 | 125.9 | 37.5 |
| 1000 | 37.9 | 26.0 | 93.3 | 3.1 | 128.1 | 39.9 |
| 1200 | 41.2 | 25.0 | 94.6 | 3.1 | 129.4 | 42.0 |
| 1400 | 44.4 | 25.0 | 97.8 | 3.1 | 132.8 | 44.9 |
| 1600 | 47.4 | 25.0 | 100.8 | 3.1 | 135.8 | 47.7 |
230/400(420) kV
| Nominal Cross Section Area |
Nominal Conductor Diameter |
Nominal Insulation Thickness |
Nominal Diameter Over Insulation |
Nomanal Lead Sheath Thickness |
Nominal Overall Diameter |
Weight |
| mm² | mm | mm | mm | mm | mm | kg/m |
| 630 | 29.8 | 32.0 | 98.2 | 3.1 | 132.8 | 38.8 |
| 800 | 33.7 | 30.0 | 98.1 | 3.1 | 133.1 | 40.2 |
| 1000 | 37.9 | 29.0 | 100.3 | 3.1 | 135.3 | 42.6 |
| 1200 | 41.2 | 27.0 | 99.6 | 3.1 | 134.6 | 44.0 |
| 1400 | 44.4 | 27.0 | 102.8 | 3.1 | 138.0 | 46.9 |
| 1600 | 47.4 | 27.0 | 105.8 | 3.1 | 141.0 | 49.7 |







